Compressor
A compressor is a mechanical flowing device designed to increase the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume.
The compressor is the main component of basic refrigeration systems and is often considered as the “heart of the cooling system”.
It works as a pump to control the circulation of the refrigerant. The basic principle of the compressor’s operation is to draw in a refrigerant vapor at low pressure and temperature from the evaporator and then compress it to high pressure and temperature.
Compressors are used in some drilling operations, in many production operations, and extensively used in surface transportation of Oil and Gas via pipelines.
Classification of compressors according to the principle of operation.
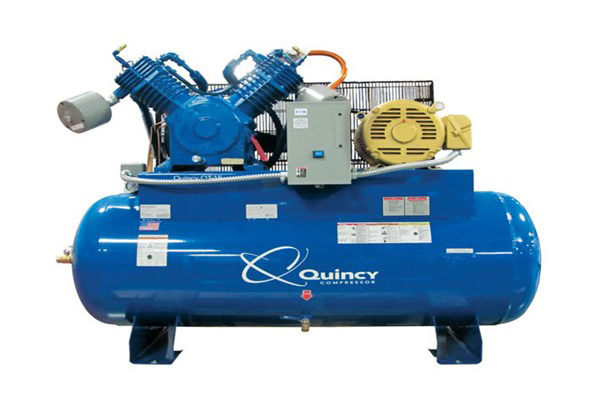

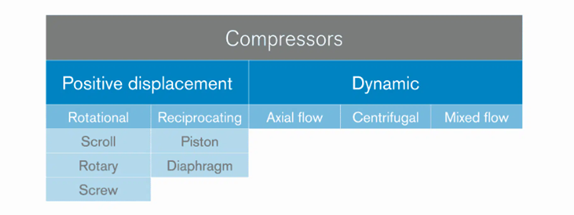

Classification of compressors by housing construction
To avoid the loss of the refrigerant during long-term operation, the compressors should be equipped with very effective seals, or even be free of all seals and openings. To describe how the compressor is enclosed and how the motor drive is situated relative to the compressed gas or vapor, we can distinguish between three types of compressors:

Mail Us WhatsApp Us